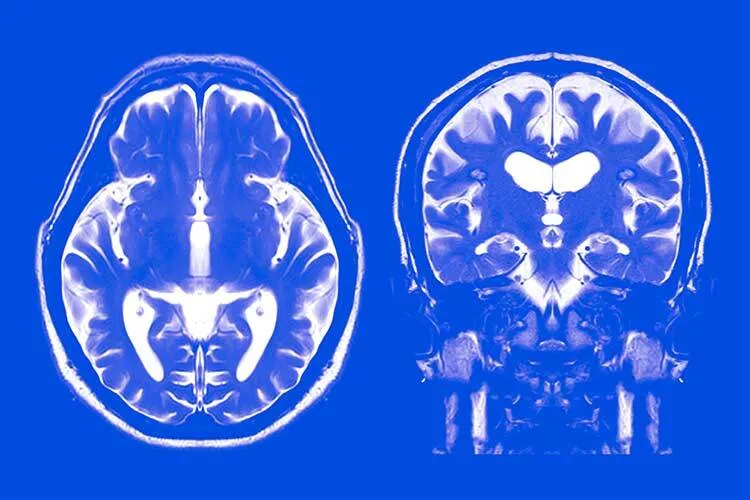
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cerebrovascular accidents such as strokes and brain hemorrhages are the second highest cause of death due to disease in the world.
Strokes occur when an artery in the brain becomes blocked by a blood clot or fat and stops the flow of blood to certain parts of the brain tissue, while brain hemorrhages occur when a blood vessel bursts.
“There are two groups of [cerebrovascular] problems: strokes, which occur in 80% of cases, and the other 20% are brain hemorrhages, which are less frequent,” explains TecSalud professor and neurologist Juan Manuel Escamilla.
The most common causes occur when a layer of fat accumulates in the arteries, which can be damaged by diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and bad habits such as smoking or −excessive− alcohol consumption.
The specialist explains that another cause is due to cardiovascular problems such as heart arrhythmias, which generate blood clots that can travel toward the brain and cause an embolism.
What happens when you have a stroke?
“The most frequent symptoms are a loss of mobility in one arm or the face, when one side of a patient’s mouth droops, difficulty speaking, and problems with coordination, such as walking badly. There can also be a sudden loss of vision,” says Escamilla.
If any of these symptoms occur, you should consider it a medical emergency and go to hospital. Treatments for the acute phase of strokes include medication that stops the blood from clotting. Severe cases require surgery to the blood vessels of the brain.
“The statistics say that 20% of patients who suffer a stroke will be fine; 50% will have some aftereffects, such as a limited ability to move one arm; and mortality is 20 to 30% in the first few days following an event.”
Rehabilitation after suffering a stroke should be started as soon as possible. This is a series of physical therapy sessions so that the patient can recover mobility or the faculty of speech.
“If someone who is 50 to 60 years old doesn’t have diabetes, doesn’t have hypertension, doesn’t smoke, and leads a healthy life, the chances of that person having a stroke are much lower,” he explains.