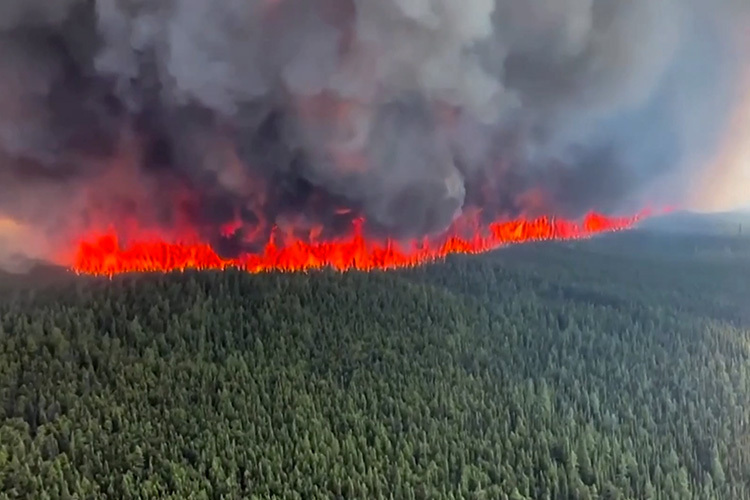
More than 400 fires in Canadian forests marked the early onset of the worst wildfire season the country has ever seen, and are causing poor air quality in Toronto, Quebec, and Ottawa, along with cities on the East Coast of the United States such as New York City, Philadelphia, and Washington.
Smoke from the provinces in western Canada has also already begun to spread into Norway and has reached as far as southern Europe.
What causes wildfires in Canada?
Anthony Taylor, a forest management specialist at the University of New Brunswick in Fredericton, interviewed by Nature, said that “the number one cause is weather.”
Fires in Canada are routine, but it has been an especially warm and dry spring across much of the country. That’s particularly true in eastern Canada, which had around 50% less spring precipitation than usual.
Piyush Jain, a research scientist with the Canadian Forest Service, says it’s unlikely to be related to an El Niño weather pattern, which brings warmer temperatures to the eastern Pacific Ocean and tends to warm the planet as a whole.
The US National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOOA) confirmed that El Niño has arrived, but the effects are expected later in the year. Still, extraordinary weather is not unexpected as the planet warms.
“Climate change is definitely a factor that is causing these extreme conditions to occur more frequently,” explains Jain.
Orange skies
On Wednesday, June 7, the concentration of PM2.5 particles in the air in New York City had exceeded WHO annual air quality benchmarks by 14 times, according to IQair, an air quality technology company that provides environmental monitoring via its website.
Sotirios Papathanasiou, a Spanish air quality specialist, reported that his “See the Air” blog about air quality had exceeded 22,000 visits on Thursday, June 8, after skies turned orange in many cities. The American media has described the scenes as evoking the Martian atmosphere on Earth.
“Many will think that this looks like a beautiful sunset but in reality, it’s a toxic sunset because it indicates the presence of tiny particles in the atmosphere and in the breathable air,” tweeted Papathanasiou in a recommendation to use N95 face masks when outside.
This unprecedented environmental pollution phenomenon is caused by the easy dispersion of tiny particles such as PM2.5 by the wind. Another peculiarity of these polluting particles is that they remain suspended in the atmosphere, which is why they present a health risk.
Particulate Matter PM2.5 are very small particles in the air that have a diameter of 2.5 micrometers. This is less than the thickness of a human hair. Particulate matter is a mixture that can include organic chemicals, dust, soot, and metals.
Another peculiarity of these polluting components is that they remain suspended in the atmosphere, which is why they represent a health risk.
PM2.5 is the smallest of respirable particles and is produced by combustion. They are so light that the wind can carry them great distances and they stay in the air for long periods.
The high concentration of polluting molecules in the atmosphere has caused the sky to turn orange and yellow because of the optical effects caused by smog.
This effect is caused by the size of the smoke particles: they are larger than the molecules that typically make up the air, which means that colors like green, blue, indigo, and violet can’t be seen, and only red can, especially its orange and yellow hues.
“Long-term exposure to PM2.5 contributes to an estimated 2,300 excess deaths from lung and heart disease each year in NYC (1 out of every 20 deaths in NYC), and short-term exposure contributes to asthma incidents severe enough to require a trip to the emergency department, as well as other health threats,” explains New York State’s official air quality site.
State Governor Kathy Hochul warned that nothing similar had been seen since the 1970s. “New York City and Syracuse were among the worst places on the entire planet yesterday,” she said in a message to the public.
“Normally, our air quality index is around 50. In New York State over the last 24 hours, and we just got these numbers in, the index hit – my numbers this morning were 200. We have updated information, it’s now 400. The index hit 400 in parts of our state. That’s an 800 percent increase,” said the governor.
Climate change knocking at the door
Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau blames climate change for this environmental problem. Almost 4.3 million hectares have been burned, which is 15 times more than the annual average over the last decade.
According to NASA monitoring carried out in the area, “there’s a high likelihood these wildfires were caused by dry lightning,” as mentioned by the account for its Short-term Prediction Research and Transition Center (SPoRT).
NASA data shows that more than 120,000 cloud-to-ground lightning strikes occurred in early June over southeastern Quebec and parts of central Ontario; NASA scientists are currently working to predict wildfires in real time.In response to the forest fires in Canada, the US space agency once again posted an explanatory video on Twitter about how climate change has caused wildfires to increase in intensity, severity, size, and duration.