Companies around the world are seeking ways to innovate on their production processes, as is the case for Siemens, which has embraced an innovative 3D printing technique known as Additive Manufacturing.
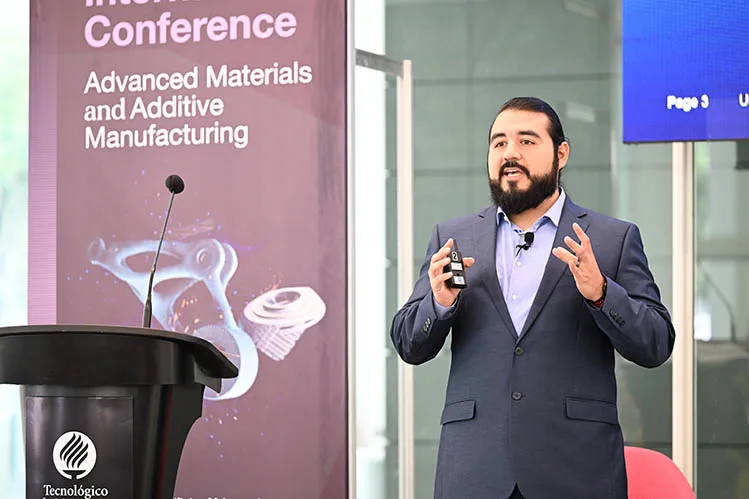
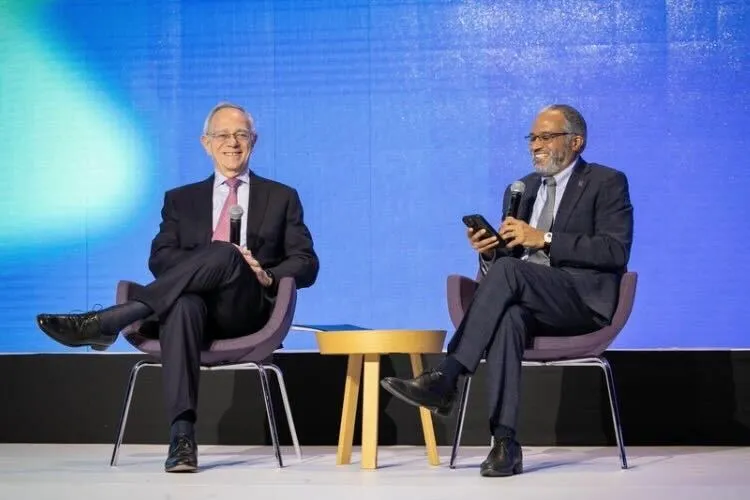
Dariel Téllez, an Additive Manufacturing research engineer at Siemens, shared the challenges and benefits of additive manufacturing and its adoption by the company during his presentation at the Second International Conference on Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing.
The engineer discussed Siemens’ experience with this type of production, the postive impact it has made within the organization, and the challenges involved in promoting and implementing this technology.
Benefits of Additive Manufacturing
Siemens is a multinational corporation that focuses on product and material development, including divisions such as the Intelligent Infrastructure division where Téllez works.
This division is largely concerned with producing goods in response to market demands, which frequently involves lengthy and multi-stage production procedures, from design to creation of functional prototypes.
According to Téllez, adopting additive manufacturing is a difficult procedure that is not always essential when there are more cost-effective and standardized methods of making items. However, there are times when this new technology becomes essential.
For instance, he presented some examples of how Siemens employed this technology; one of them was due to a nylon shortage, which might have exhausted their inventory of a high-voltage circuit breaker and halted their production line.
Another example consisted of reducing the creation time for a prototype of a residential circuit breaker that had previously taken eleven months to create. The procedure was cut down to five months by using additive manufacturing-created pieces.
The Benefits and Difficulties of This Technology in Business
Dariel Téllez highlights some of the benefits, such as quicker and easier prototyping, better design flexibility, and the possibility of merging numerous components into one, eliminating the assembly phase and assuring equivalent or even enhanced qualities.
It additionally allows the production of parts or components that are uncommon or complex, which would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional methods.
However, Téllez underlines the need to raise awareness of the usage of this technology, ensuring that company executives and leaders are not hesitant about including it in their operations.
Another problem is ensuring the quality and certification of manufactured components and processes since there are specific verification procedures for materials and parts printed using 3D technology, which needs frequent monitoring by independent laboratories. “This is just the beginning, and we are establishing numerous synergies with industry and universities to continue our research,” Téllez concluded.