Powder materials, in the field of additive manufacturing, could improve and optimize construction processes in various fields, such as the aerospace industry or the production of prostheses for the medical field.
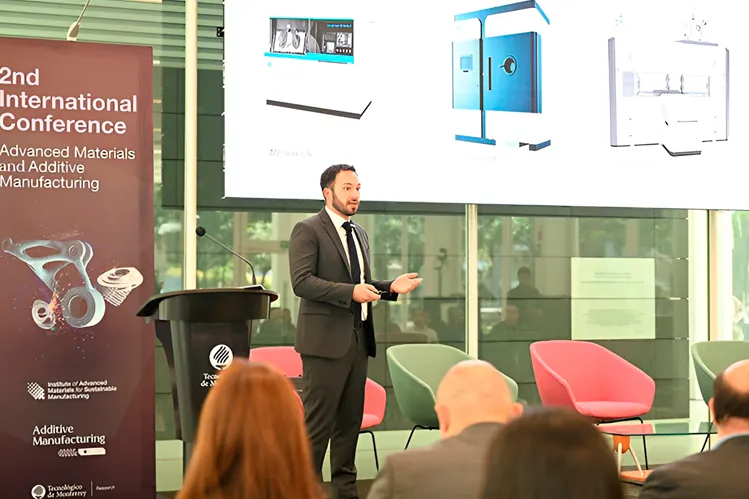
During the second day of the Second International Conference on Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing organized by the Institute of Advanced Materials for Sustainable Manufacturing, Daniel Frydryk, Senior Research Engineer of Materials Applications and Behavioral Engineering at GE Additive, the machine manufacturing arm of the multinational company General Electric, explained those that he considers to be the most promising.
Additive manufacturing is the technology used in 3D printing that allows the manufacturing of three-dimensional parts and objects through successive printing of layers of some material.
Some advantages are that it makes it possible to use only the necessary amount of material, thereby minimizing waste. In addition, it is possible to design complex geometric structures that would be practically impossible to achieve with conventional techniques.
Three Innovations in Additive Manufacturing
According to the researcher, there are three innovations that we should follow closely in the world of additive manufacturing and they are all based on using powder materials, either ceramic-based (such as glass or pulverized plaster) or metal-based (such as powder-coated stainless steel).
“One of the most rewarding things about my job is that I get to work on these three advancements with any client that walks through the door,” Frydryk said.
The first is the technique called Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion (EB-PBF). This is an additive manufacturing technique that is based on depositing successive layers of powder materials to fuse them with an energy source, in this case, an electron beam, something very similar to a laser that fires electrons instead of photons.
The process allows an improvement in the control of the microstructure and mechanical properties of built objects.
The second is Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (LB-PBF), which is similar to the previous one but with a laser. This allows for optimization in the construction of objects that need to be cut with a laser.
The third and last is Binder Jetting, a 3D printing technique that consists of depositing an adhesive binding agent on thin layers of powder material. This process helps to perfect the shape of the built parts and optimize their structure.