Due to the boom in manufacturing innovation in Mexico and its close ties with companies and the Latin American and North American markets, Tec de Monterrey announced the creation of its latest specialized laboratory, the Additive Manufacturing Core Lab, during the inauguration of the Second International Conference on Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing.
This Core Lab will focus on designing and fabricating materials for industry, as well as attending to and providing specialized services to researchers from the institute itself and companies and other institutions.
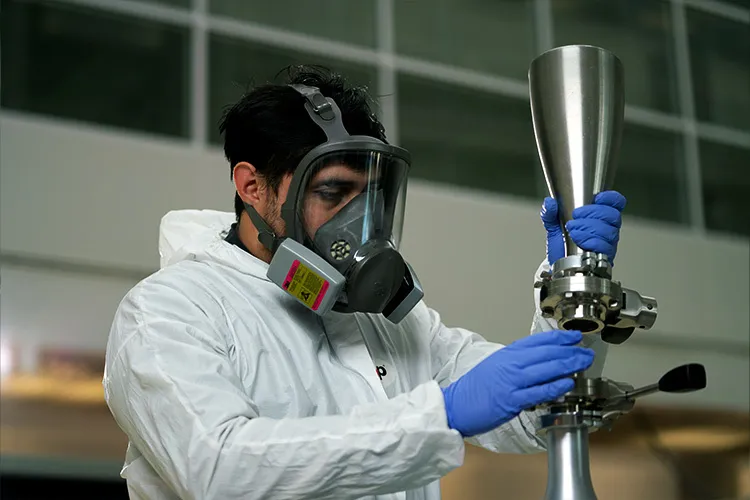
Additive manufacturing is a revolutionary technology that enables the fabrication of parts and components that usually have complex geometries through the printing of successive layers, thereby minimizing material waste and providing a sustainable option.
“We want to fulfill industrial demand by developing integrated solutions, by fabricating functional and disruptive prototypes and products fabricated with advanced and sustainable materials,” said Óscar Martínez, leader of the Core Lab and member of the Institute of Advanced Materials for Sustainable Manufacturing.
The Core Labs are a laboratory initiative at Tec de Monterrey, of which Additive Manufacturing is the latest, alongside Genomics, Data Science, and a Preclinical Research unit.
“We’ve focused our attention on research as an essential process for improving the quality of education, to make the university relate to humanity’s real problems, thereby improving the lives of our fellow citizens,” said Guillermo Torre, Rector of TecSalud and Vice President of Research at the Tec.

Additive Manufacturing Core Lab
One of the Additive Manufacturing Core Lab’s main objectives is to provide an option for nearshoring in the wake of changes to company production chains that occurred rapidly due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
These changes have led to international companies moving their supply chains to places like Mexico due to their proximity to the North American and Latin American markets, which is why additive manufacturing has become more important.
This laboratory will be open for industry and academia to manufacture parts and components through 3D printing, create prototypes, and investigate inputs such as the powders used for printing.
Another of its main objectives is to promote the education of human capital that is highly specialized in this technology, which means not only providing students with knowledge but also identifying and developing technological solutions that make a positive impact on society.
The laboratory will offer training programs on various innovative additive manufacturing techniques, as well as on developing new materials employed in this type of printing.
It will also strive to set itself apart at national and international levels through a focus on advanced technology transfer, which it will do by creating prototypes and accelerating technology-based companies.
“We want to consolidate ourselves as a global point of reference for research and innovation in the development of functional industrial prototypes and materials, playing an essential role in additive manufacturing in Mexico and worldwide,” explained Martínez.
The Core Lab will have state-of-the-art equipment and in the first phase will offer 3D printing services through a technology known as direct metal laser sintering, which uses a variety of materials and has a precision of 0.015 millimeters and a maximum construction volume of between 245 and 300 millimeters.
What will the Core Lab include?
Specialized machinery has already been installed in the Core Lab, such as the M2 Series 5 and MLab 200R, the latter of which can print reactive materials such as titanium and aluminum, which were acquired from the GE Additive company, a General Electric subsidiary that is dedicated to this technology.
In its first phase, this laboratory will offer printing services for functional 3D prototypes in superalloys based on nickel, titanium, and cobalt, as well as traditional materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and martensitic steel (stainless steels alloyed with chromium and other elements).
“The Core Lab plays an important role because it’s a place that connects society’s needs with Mexican talent supported by industry and the government. It’s a unique way of addressing current challenges, developing a virtuous ecosystem between industry, academia, and government that enables the acceleration of innovation,” said Gabriel Francisco Arreola, Site Operations Manager & Government Relations at GE Additive.
Collaboration Strategies
Óscar Martínez said that this space aims to be a meeting point between industry, educational institutions, technology providers, and end users, to promote additive manufacturing in Mexico and worldwide.
Its main audiences include research groups, who are looking for options and spaces to accelerate and innovate on the fabrication processes of functional prototypes and technological solutions that can be scaled up.
It will also be a space for undergraduate and graduate students whose research focuses on production, as well as public administrations that request the laboratory’s services.
Industry is another of the Core Lab’s audiences, with whom it plans to collaborate in areas ranging from fabricating prototypes and creating components to accelerating and scaling up technology for a specific market.
For instance, it is seeking to establish partnerships with leading companies such as GE Aviation, NTU, and Renishaw, as well as public and private universities and research centers that are interested in scientific development and technology.
“We have to be prepared for the global challenges that are arising due to the phenomenon of nearshoring. There is a global standard demanded of us. As we aspire to compete, we need committed and talented men and women,” explained José Alfredo Perez, Director General of the Nuevo León Institute of Innovation and Technology Transfer.
Tags: International Conference on Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing, Core Labs, Institute of Advanced Materials for Sustainable Manufacturing, additive manufacturing, Second International Conference on Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing